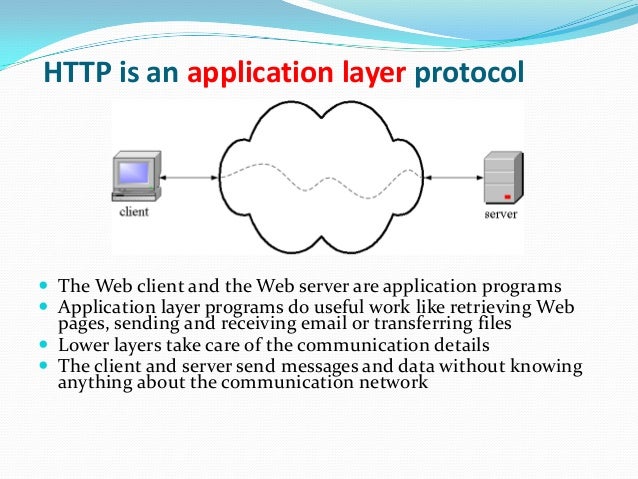
1) HTTP : Hypertext transfer protocol
- It is used to view webpages in the internet.
- All information is sent in Clear text.
- Vulnerable to hackers.
- Cannot use this protocol to share personal information (Personal details, Bank details)
2) HTTPS: Secure Hypertext transfer protocol.
- Encrypts the data that is being retrieved by HTTP.
- Uses encryption algorithms to scramble the data that’s being transferred.

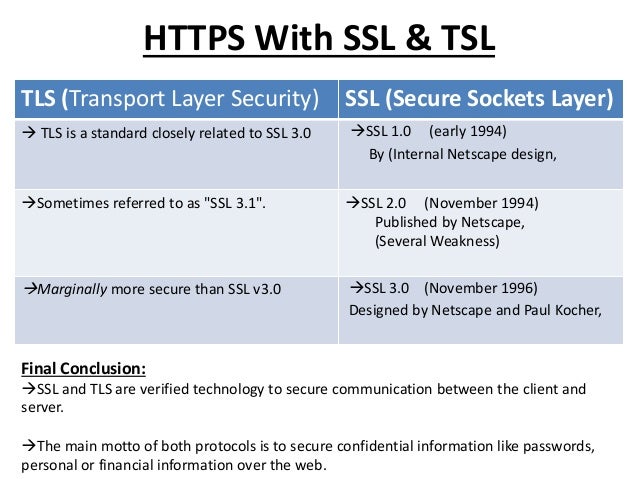
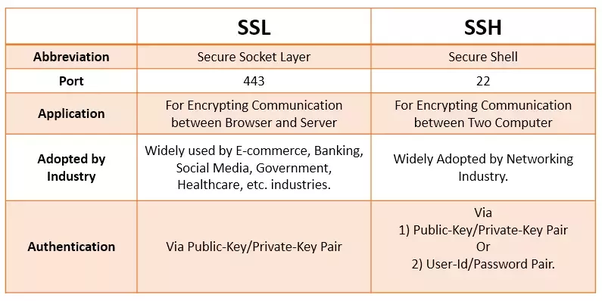
3) SSL : Secure Socket Layer Protocol.
- It is a protocol that’s used to ensure security on the internet.
- Uses public key encryption to secure data.
- An SSL Certificate is used to authenticate the identity of a website.
4) TLS : Transfer Layer protocol.
- The latest industry standard cryptographic protocol.
- The successor to SSL.
- Authenticate the server, client and encrypts the data.
- There are websites which are still using HTTPS. If the there are not using SSL protocol, then google will penalize that website in their search rankings.